We recently read that the UV lamps used for gel — and
sometimes dip — manicures could raise chances of getting cancer. So,
is that true? Are there any alternatives?
اضافة اعلان
Gel manicures are popular because they last a long time and do
not easily chip or peel. But they have come under scrutiny in recently
following a new study that found that the ultraviolet lamps used for these nail
treatments damage cells in ways that could potentially increase the risk for
cancer.
 (Photos: Envato Elements)
(Photos: Envato Elements)
The findings add to a small but growing body of research
suggesting that regular use of UV nail lamps could accelerate aging and
increase cancer risk. Health experts agree that UV light causes damage to skin
cells, but there is still not enough data to determine just how dangerous the
occasional gel manicure might be, said Dr Chris Adigun, a dermatologist in
Chapel Hill, North Carolina, who was not involved in the study.
“We can’t quantify the risk,” she said.
Still, Adigun and other dermatologists said that taking certain
precautions can help make gel manicures safer. Dip powder manicures are another
option, though they may not be entirely risk-free, either.
UV radiation in nail lamps
UV lamps are essential for gel manicures because the light makes
the nail polish harden and become more durable. (Some salons use LED lights for
gel manicures, but these release plenty of UV light, too, Adigun said.)
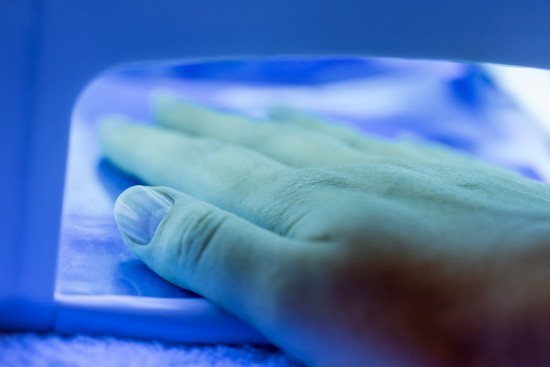
In the new study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature
Communications last month, researchers exposed human and mouse cells to
radiation from a nail lamp used in many US nail salons.
When the cells were exposed to UV light from the lamp for 20
minutes, around 30 percent of the cells died. Some of the cells that survived
suffered damage to their DNA. The damage patterns that researchers observed
were similar to those seen in people with melanoma, a potentially deadly type
of skin cancer, said Maria Zhivagui, a co-author of the study and a
postdoctoral scholar of cancer genomics and public health at the University of
California, San Diego.
Although the cell damage is worrying, Zhivagui said, the study
does not prove that UV lamps can cause cancer. Cells in a lab are more
vulnerable to damage than cells on a person’s hand, which has a thick outer
layer of skin made of dead cells that helps protect against environmental
damage, Adigun said.

No major studies have yet evaluated whether people who get gel
manicures are more likely to develop skin cancer than people who don’t. There
have been case studies involving people who were diagnosed with skin cancer on
their hands after getting gel manicures regularly, but it’s unclear whether
their nail treatments were the culprit.
Still, “the data is mounting that UV radiation emitted by nail
lamps could be potentially dangerous,” Adigun said.
The powder alternative
One alternative is the dip powder manicure, which is also
long-lasting and involves dunking nails into acrylic powder after applying an
adhesive. A dip manicure typically does not require a UV lamp, but some
stylists might add an extra gel coating at the end so that the manicure lasts
longer — in which case a UV lamp would be used, said Dr Lyndsay Shipp, a
dermatologist based in Oxford, Mississippi.
There is one concern with dip manicures, though: Stylists often
use the same jar of acrylic powder for multiple customers, which increases the
possibility that the powder could harbor germs that cause nail infections,
Adigun said.
But Adigun, who has specialized in nail disorders for over 16
years, said that she had never heard of anyone getting a nail infection from a
dip manicure. And the acetone that stylists often use to remove nail polish at
the beginning of a manicure acts as a disinfectant, Shipp said, cleaning the
nail and reducing the chances of contamination.

The risk of getting an infection from a dip manicure is
“incredibly rare,” Shipp said.
Safety tips for your next manicure
Thankfully, there are steps you can take to minimize health risks
the next time you visit the salon.
If you are getting a gel manicure, consider wearing fingerless
UV protective gloves, Adigun said. (She did not recommend using sunscreen, as
sunscreens have been shown to protect against UV exposure only from the sun,
not from UV lamps, she said.)
To reduce your risk of infection, Adigun suggested asking your
stylist not to push back or remove your cuticles, which provide an important
barrier against germs. Many people blame post-salon infections on contaminated
equipment, she said, when it’s more likely that their own germs infected the
nails after their cuticles were removed.
“Tell them, ‘Please trim my nails, file my nails, do not touch
my cuticles,’” Adigun said.
It is also a good idea to request that your stylist only lightly
buff and file your nails before adding polish, Shipp said, because heavy
buffing and filing can make them thinner and more brittle. Thick coats of
polish can also weaken nails, she said, so it’s best if stylists apply thinner
layers. Also, skip the gel topcoat if you’re getting a dip manicure so you do
not have to use a UV lamp.
And it may seem obvious, but pick a salon that takes safety
seriously, Shipp said. Ask if the staff members reuse equipment and, if so, how
they sanitize it between customers. (Autoclaves or dry-heat sterilizers are
ideal.) You could also purchase your own drill bits, files and buffers and
bring them with you, she added.
Although gel and dip manicures can pose risks, they don’t have
to be a source of anxiety, Adigun said, adding, “It’s all about having the
information you need to be able to go in there and get a great manicure or
pedicure safely.”
Read more Health
Jordan News







