Maintaining a
healthy body weight should be a priority for
everyone. The more overweight you are, the greater the risk of developing
certain diseases, such as diabetes. Being overweight may also have a negative
impact on mental wellness, by leading to depression and poor body image.
اضافة اعلان
In 2020, 51 percent of the population aged 18 – 44 in Jordan
was considered overweight or obese.
There is no easy way to lose weight, contrary to what many
marketing schemes say. Still, there are ways to help make the journey easier
and encourage one to see it through.
How to determine a healthy body weight
Understanding your body is important; one of the first steps
in doing so is determining what body weight is considered healthy for you.
There are different methods to calculate this, but the most
commonly used calculation is that of the body mass index. Finding out the BMI
is a simple calculation. You divide your weight into your height squared and
you get a double-digit number that is likely in the 20s. A BMI between 18.5 and
lower than 25 is considered a healthy range. Those between 25 and less than 30
are overweight and greater than 30 is considered obese.
The BMI is the preferred factor for determining a healthy
body weight in the average person, because it has been found to have a good
correlation to fat mass.
 (Photo: Envato Elements)
Metabolism and calories
(Photo: Envato Elements)
Metabolism and calories
Our body is a complex machine with many internal processes.
It normally understands exactly what it needs and how much of it. One of its
most important processes is metabolism, which is often misunderstood.
Metabolism is the process by which the body converts food
and other forms of sustenance into energy. This energy comes in the form of
calories and the amount needed per day depends on a host of factors. Our body
is in constant need of energy, even while at rest, for basic living functions
such as breathing, repairing cells, and circulating blood.
Metabolism that happens during rest time is known as the
basal metabolic rate (BMR) and it is important in understanding how many
calories your body needs. The calculation for basal metabolic rate requires
weight in kilograms, height in centimeters, and age, and goes as follows:
Men: 66 + (13.7 × weight in kg) + (5 × height in cm) – (6.8
× age in years)
Women: 655 + (9.6 × weight in kg) + (1.8 × height in cm) –
(4.7 × age in years)
For example, a 35-year-old male who weighs 80 kg and is 180
cm tall will require approximately 1,825 calories per day in order to maintain
basic life functions. However, this value is only an estimate and there are
many factors that can affect it, such as muscle mass, temperature, genetics,
and certain supplements. Furthermore, this does not consider the additional
calories needed to perform daily physical activity.
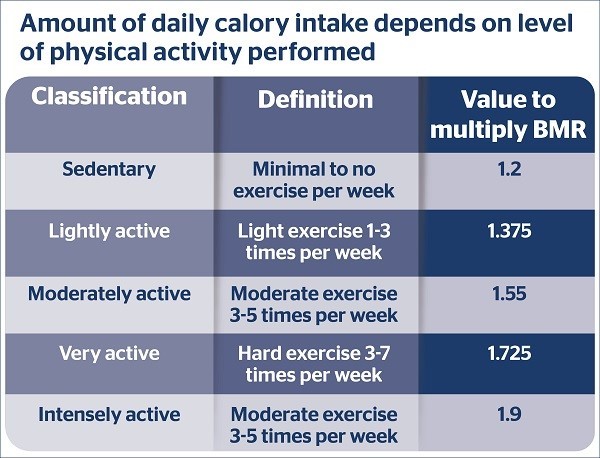
The amount of calories needed every day depends on the level
of
physical activity you perform on average and can be classified into five
categories. Depending on your classification, you will take your basal
metabolic rate and multiply it by a value. The result will give you how many
calories are needed each day in order to maintain your body weight.
Using the previous example, if a male is moderately active,
he requires roughly 2,500 calories per day in order to maintain his body
weight. When it comes to weight gain, metabolism is rarely ever to blame.
The amount of calories needed to sustain yourself are
relative to your body’s needs. Factors such as genetic makeup and hormonal
control may also explain weight gain, but are also rare. Ultimately, diet and
the impact of environment on lifestyle, which includes sleep, physical
activity, and stress, are the main predicators for weight gain.
Fat burning
Everyone knows that the more you eat, the more weight you
gain. The fundamental principle behind this is an imbalance between calorie
intake and calorie expenditure. When calorie intake is higher than calorie
expenditure, this results in excess calories. In general, there are three
options the body has with calories: metabolize, excrete, or store.
Ideally, the majority of foods consumed should be
metabolized, meaning that it is converted into energy for the body to readily
use. The body is not 100 percent efficient at absorbing all the nutrients from
foods and a percentage of the potential source of calories is excreted as
feces.
 (Photo: Envato Elements)
(Photo: Envato Elements)
Finally, a portion of calories is stored as fat that can be
used later in periods when food becomes scarce. This last process served our
ancestors well as it allowed them to go extended periods without food without
starving. In modern times, most do not have difficulty finding food and, on the
contrary, we tend to overeat. This ultimately results in more calories being
stored. In order to burn fat, the opposite should be true.
Creating a calorie deficit, in theory, will cause our bodies
to use up all the readily available calories from the food consumed that day
and get the rest from fat that is stored. In order to create a calorie deficit,
calorie expenditure should be greater than calorie intake.
Difficulty losing weight
Anyone who tried to lose weight will tell you that it can be
difficult. Although progress can be made at first using a calorie deficit,
people often hit a plateau and weight loss seems to stop.
There are a few different theories to explain this but one
of the most popular is the hormone hypothesis. In nearly all the foods we eat,
there are important macronutrients known as
carbohydrates or carbs. Carbs are
complex sugars; most all are broken down inside the body to a simple sugar known
as glucose. After a meal, especially one dense in carbs, the blood is filled
with glucose and the body needs to balance it. In response, the body releases a
hormone known as insulin, which pulls the sugars out of the blood and stores
them in
skeletal muscle, the liver, and fat cells. If insulin levels remain
high, fat cells retain fat, and the body will preferentially burn glucose
instead of fat. Based on this hypothesis, it is important to avoid increasing
insulin levels. There are many ways to do this and many diet plans center
around this concept, such as the ketogenic diet, which consists of high protein
and fats diets while avoiding carbohydrates.
Read more Health








